Simply explained
20 June 2018
1 minute
The track maintenance
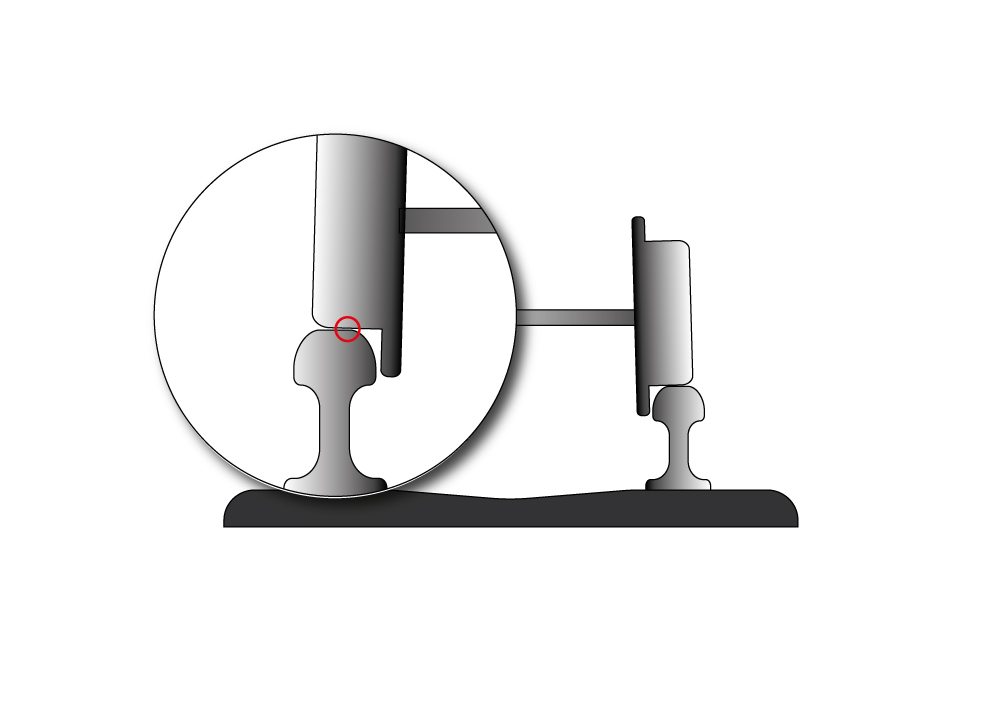
The rail plays two important roles: direct support of rolling loads and steering of the rolling stock. The rail must also fulfill three conditions: resistance, ride comfort and noise level reduction. In order to ensure the latter , the rails are regularly examined from every angle.
- In order to ensure the longevity of the rails and to eliminate any risk of breakage, rail maintenance is essential. (1/2)
- In order to ensure the longevity of the rails and to eliminate any risk of breakage, rail maintenance is essential. (2/2)
- The brigade chief conducts regular inspection tours and intensively controls heavily used areas.
- Inspection of the rails and welds by ultrasound (internal structure) and eddy current (rail surface) to detect cracks and chips. (1/3)
- Inspection of the rails and welds by ultrasound (internal structure) and eddy current (rail surface) to detect cracks and chips. (2/3)
- Inspection of the rails and welds by ultrasound (internal structure) and eddy current (rail surface) to detect cracks and chips. (3/3)
- Preventive and systematic grinding of high stress areas to maintain the railhead and effectively correct defaults. (1/2)
- Preventive and systematic grinding of high stress areas to maintain the railhead and effectively correct defaults. (2/2)
- Aluminothermic welding is used to ensure the continuity of the railway tracks when they have to be replaced. These welding operations avoid transitions that would represent a weak point of the tracks and thus affect ride comfort. (1/2)
- Aluminothermic welding is used to ensure the continuity of the railway tracks when they have to be replaced. These welding operations avoid transitions that would represent a weak point of the tracks and thus affect ride comfort. (2/2)